The Advice Paradox: Why Following Your Heroes Often Backfires
Why the Advice From Our Heroes Often Contradicts The Paths That Made Them Successful (And How To Avoid The Trap)
We idolize successful entrepreneurs and public figures. We read their books, listen to their podcasts, and take their words as gospel.
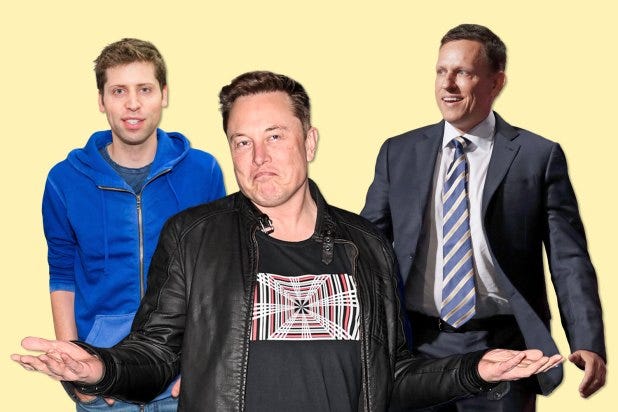
When Elon Musk says to shoot for the stars and change the world, we feel inspired. When Peter Thiel questions the value of college, we feel validated for skipping class. And when Sam Altman advocates raising tons of money and building a big team, we rush to emulate him.
This makes sense - we all want to learn from those who have achieved greatness. But here's the paradox: often, the advice successful people give doesn't align with the path that got them to where they are.
In this deep dive, we'll explore why this "advice paradox" happens, see examples of how following heroes can backfire, and provide frameworks to avoid falling into the trap yourself.
The Core Advice Paradox
First, what exactly is the "advice paradox"?
It's when...
1) A successful person advocates for a certain approach or mindset.
But...
2) That advice contradicts the real-world steps they took to become successful themselves.
Some examples:
- Elon says work on solving big problems, but he actually got rich quick with web startups first.
- Peter Thiel questions college, but has multiple prestigious degrees himself.
- Sam Altman pushes big moonshot projects, but started with small steps first.
In other words, the advice sounds great in a tweet or inspirational quote, but doesn't hold up when examined against their actual path to success.
Why does this happen? A few key reasons:
1. Simplification - They condense their complex journey into easy-to-grasp advice. Nuance is lost.
2. Hindsight Bias - Failures fade, victories remain. The ugly struggles behind the scenes get glossed over.
3. Projection Bias - Successful people sometimes advise their younger selves rather than their audience.
4. Survivorship Bias - We only hear from the success stories, not the many who took the advice and failed.
5. Confirmation Bias - We crave their advice because it confirms our existing beliefs and desires.
6. Missing Context - Public advice lacks personal details of their path that made it work.
Combined, these biases warp the advice and our ability to apply it rationally. We hear what we want to hear from those we look up to, ignoring inconvenient truths.
Let's examine a few real-world examples of the advice paradox in action to ground this:
Case Study #1: Sam Altman and Y Combinator
Sam Altman is famous for being the former President of Y Combinator (YC), one of the most prestigious startup accelerators. He stepped down in 2019 after many successful years at the helm.
He was also the founding CEO of OpenAI, the billion-dollar artificial intelligence research lab backed by Elon Musk, Reid Hoffman and others.
Recently, he's been questioning elements of YC's traditional startup advice:
- He said founders shouldn't always focus on growth at the expense of business model early on.
- He discussed how raising too much money too fast can be dangerous.
- He suggested today he might not advocate starting with something small and iterating.
Much of this runs counter to YC's standard guidance. For example, growth at all costs is a well-known YC mantra.
Sam's thoughts are evolving. But it's worth looking back at his actual path:
- He started with YC itself, launching a small startup called Loopt out of the program.
- Loopt focused on growth first and monetization second per YC's advice.
- He built his reputation and network through YC before launching OpenAI.
In other words, he followed the "standard" YC playbook himself before later questioning it. His early steps align more with YC's traditional advice rather than his current evolved perspective.
The lesson here: recognize that advice develops over time as we gain experience. What served well early on may need rethinking later as the landscape changes. Be wary of those quick to criticize the very systems they used to achieve success.
Case Study #2: Elon Musk's Winding Road
Elon Musk is larger than life. Millions idolize him for his grand ambitions and unprecedented accomplishments.
But unlike most heroes, Elon is quite transparent about his past. He's open about his winding path of failures and triumphs.
Still, the way he discusses his journey can distort the truth:
Elon emphasizes the bold vision. He makes starting hard tech companies sound exciting, attainable, and the obvious path.
In reality, he took a more convoluted route:
- He left Stanford after 2 days to join the dot com boom in the 1990s.
- His goals were practical - build profitable companies as fast as possible.
- He started with Zip2, a software company acquired for $300M. No rockets involved.
- He then co-founded PayPal, pivoting from money transfers to payments. It sold to eBay for $1.5B.
Only after two big exits did he have the resources to go all-in on SpaceX. Even then, early rocket launches famously failed. It took grinding persistence to inch toward success.
And even today, his grand ambitions depend on funds from his earlier wins. For example, he has continually invested his personal PayPal fortune into Tesla to keep it going.
Elon's advice comes from a place of passion and idealism. He aims to inspire the next generation to shoot for the stars.
But behind the scenes, pragmatism and baby steps paved the way. As outsiders, we underestimate the gritty determination and simple economics underpinning his dreams. His journey remains more earthbound than one might guess.
The takeaway: temper ambition with realism. Celebrate visionaries, but don't overlook the humble beginnings supporting their ascent. Plot your own incremental stepping stones to turn lofty goals into reality.
Case Study #3: Peter Thiel's Contrarian Path
Few figures spark more debate lately than Peter Thiel. As PayPal's co-founder and one of Facebook's earliest investors, his success speaks for itself.
But his controversial views make applying his advice tricky:
- He actively questions the merits of college and traditional education.
- He criticizes Silicon Valley's conformity and lack of innovation.
- He urges startups to solve big problems outside petty tech.
Yet again, his background reveals notable contradictions:
- Thiel has both undergraduate and law degrees from Stanford, the heart of Silicon Valley.
- He worked at a New York law firm and investment bank early in his career - hardly radical paths.
- His early successes, PayPal and Facebook, emerged from the very tech ecosystem he now critiques.
- Even his famed criticism of college came only after he had already extracted value from multiple degrees.
Thiel provokes important discussions. But his views often run opposite his lived experience.
This demonstrates how the messaging of successful contrarians can outpace reality. By nature, contrarians contradict the norm to stand out. But this breeds ironic tensions between their advice and background.
When evaluating contrarian viewpoints, look beyond the headlines to fact check claims against real-world behavior. Sift signal from noise.
Key Takeaways
Stepping back, a few core lessons emerge:
1. Map advice back to the adviser's actual path critically and comprehensively before following.
2. Temper extreme opinions with moderation and incremental progress.
3. Adapt advice to your specific context vs. applying it wholesale.
4. Challenge your own biases when seeking out opinions that merely confirm your preexisting worldview.
5. Take a long-term view - lasting success emerges from sustained small gains over time.
In Sum
We opened with a seeming paradox - that the advice from many heroes contradicts the steps that led to their success.
Upon reflection, the contradictions make sense. Messy reality gets distilled into clean narratives. Nuance and struggle give way to simple stories and inspiring soundbites.
This phenomenon is neither malicious nor unique to entrepreneurs. It is simply human nature in action. We must recognize our own tendency to simplify, forget and reframe the past in a favorable light.
But with context, the core principles revealed are sound:
Work incrementally toward ambitious goals. Master fundamentals before chasing unicorns. Stay grounded through ups and downs. Learn from history, then write your own story.
No blueprint guarantees success. But armed with awareness and guided by those who came before, we can avoid their pitfalls while benefiting from their wisdom.
With eyes wide open, we forge ahead. The journey continues...